Feb 5, 2025 2:09:05 PM
The potential applications of nanoemulsions are vast and varied. In..
Nanoemulsions are two or more immiscible liquids (normally consisting of an oil and an aqueous phase) where one is finely dispersed in the other forming nano scale droplets.
Find out how we help manufacturers achieve stable nanoemulsions.
Stable, small uniform particle sizes with tight distributions are crucial for sterile filtration, increasing bioavailability and stability for pharmaceutical industry. This is vital in producing successful parenteral emulsions including Vaccine Adjuvants, which can be used in the fight against seasonal flu and pandemic influenza, and other injectable formulations, as well as ophthalmic emulsions.
Microfluidics® technology delivers not just the highest shear forces, but also applies it uniformly to ensure that every mL of material undergoes the same high shear rates, no matter whether it is 1mL at a time or many liters per minute, to achieve nanoemulsions with tight particle size distribution.
We have a wide range of Microfluidizer® processors that are simple to use and clean with the option of conforming to cGMP requirements. Our nanoemulsion formulation solutions are trusted for research, development and production in different applications across the globe.
Microfluidics has over 40 years of application development and machine engineering experience to help drive your product to market as quickly as possible. Not only is our technology repeatable but it can be seamlessly scaled from small scale volumes to large commercial capabilities.
Microfluidizer® technology is critical for any nanoemulsion application that requires precise control of the particle size.
Microfluidizer® technology has been proven to be ideal for creating nanoemulsions not least because it can increase emulsion stability and facilitate efficient sterile filtration.
Additionally, samples as small as 2 mL can be processed with an assurance that this can be scaled up to hundreds of liters per hour on the production scale machines with the same results due to the fixed geometry Interaction ChambersTM found on each model.
The following are just some of the examples of common nanoemulsions produced using Microfluidizer® processors.
There are many proven nanoemulsion applications in a variety of industry sectors including:
Some of the most effective vaccine adjuvants are nanoemulsions incorporating squalene, notably MF59 (produced by Seqirus) and AS03 (produced by GSK). Microfluidics has been collaborating on vaccine adjuvant research with the Access to Advanced Health Institute (AAHI), previously known as the Infectious Disease Research Institute (IDRI), and have proved a repeated particle size target for enabling sterile filtration of the nanoemulsions.
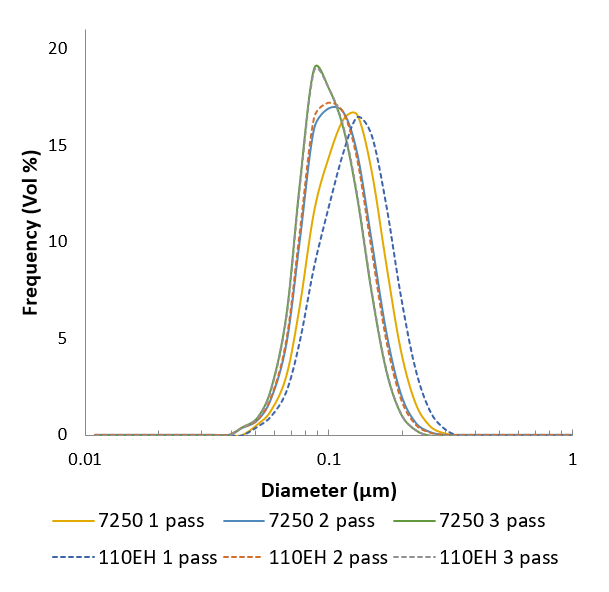
Here’s an example of particle size distributions that were achieved using the Microfluidizer® technology first developed on the lab-scale M110EH, and then scaled up to the production scale M7250.
As an intravenous (IV) sedative-hypnotic that is used in ICU departments in hospitals for sedation of intubated, mechanically ventilated patients, Propofol proved to be vital in the fight against COVID-19. Due to its very low solubility in water, propofol is usually formulated as a lipid emulsion like many other active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) such as Aprepitant, Clevidipine Butyrate, Difluprednate, Cyclosporin, Latanoprost, etc.
Microfluidics® processors are successfully used in the manufacturing of propofol. After processing, the propofol liquid reaches the target particle size with a tight particle size distribution.
The manufacturing process can easily be scaled up. Tests were run in our lab using the M110EH pilot-scale machine and then using the M7250-30 production scale machine.
Results showed that the particle size in the propofol liquid obtained on the production machine was very close in size to that obtained on the pilot machine. Thereby proving the scalability.
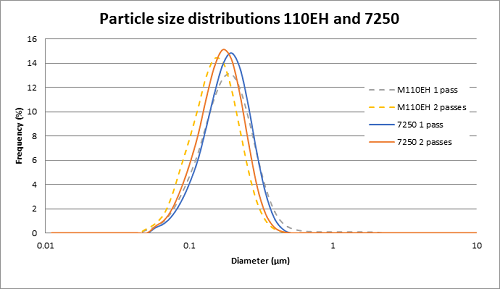
Nanoemulsions are an important drug delivery mechanism.
Both drug delivery and vaccine adjuvant nanoemulsions must be sterilized. Different strategies are available and include autoclave and gamma irradiation. But sterile filtration is one of the least expensive and most gentle sterilization methods available.
In order to pass nanoemulsions through sterilizing filters without losing product or clogging the filters, it is really important to have very narrow particle size distributions with virtually all of the particles less than 220 nm, which is the rated membrane pore size of sterile grade filters.
This phenomenon was first detailed by biotechnology company CORIXA. They found that in the sterilizing process they were losing a considerable amount of material of their nanoemulsion that was produced on a homogenizer.
The solution was validated in collaboration with Pall Life Sciences. Pall had approached Microfluidics to understand why nanoemulsions produced with Microfluidizer® technology resulted in more robust sterile filtration processes.
To demonstrate the importance of particle size distribution, Microfluidics produced a range of nanoemulsions of differing particle size and size distributions.
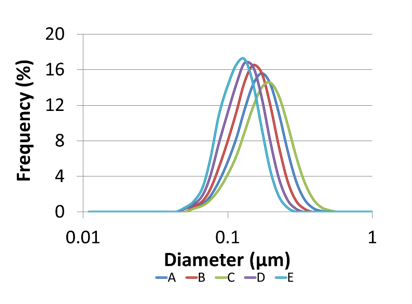
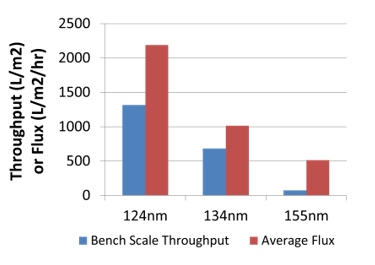
Pall then used their sterile grade filters to investigate the throughputs in relation to the particle size distributions.
The samples filtered were then analyzed to verify that all the bacteria had been removed.
With over four decades of expertise in application development and machine engineering, our technology has been refined to deliver high shear forces consistently. Our experts are dedicated to helping to helping oiur customers reach their production goals and scale up to larger volumes. Get in touch to learn more about how we can help.
There are many benefits to producing nanoemulsions with small average size and narrow particle size distributions.
Instability and phase separation of emulsions and suspensions are common challenges. Research and production teams find it problematic creating nanoemulsions that are stable. This is because most technologies cannot produce the particle size distribution necessary to reach the product goals.
To overcome these issues, Microfluidizer® Processors use a unique fixed-geometry Interaction ChamberTM to reduce particle sizes uniformly and to a level unmatched by other methods. This enables customers to not only optimize formulations and achieve stability, but to also enjoy the cost efficiencies offered by products with a prolonged shelf life.
These stable emulsions achieved with the Microfluidics equipment mean that it is possible to create a translucent appearance for cannabis, food or cosmetic products.
Creating nanoemulsions with Microfluidizer® technology produces world-class results.
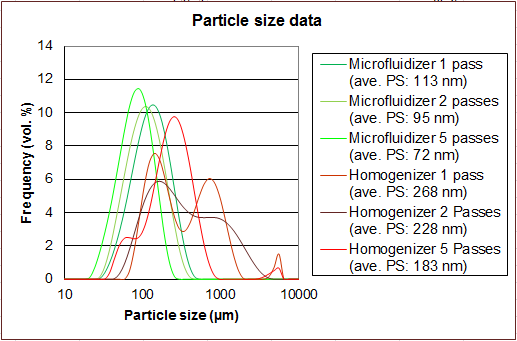
Microfluidizer® high shear fluid processors are frequently compared to conventional homogenizers because they are used in similar applications. However, the results achieved can be dramatically different.
Opposite is a comparison of a nanoemulsion that was processed on a Microfluidizer® Processor compared to a High Pressure Homogenizer. All the samples were processed at 30,000 psi.
Microfluidizer® Technology |
Conventional Homogenizer |
|
The Interaction ChamberTM and pumping system provides a uniform high shear environment for the product stream during processing. This ensures repeatable results with particle sizes on target with tight particle size distributions. The process is also reliably scalable. Learn more about how our technology works. |
Homogenizers use variable-geometry valves as the shear mechanism alongside a constant volume pumping system which does not precisely control the processing environment. Product is thereby exposed to significantly more variations in shear which results in larger average particle sizes, a wider distribution and scaleup challenges. |
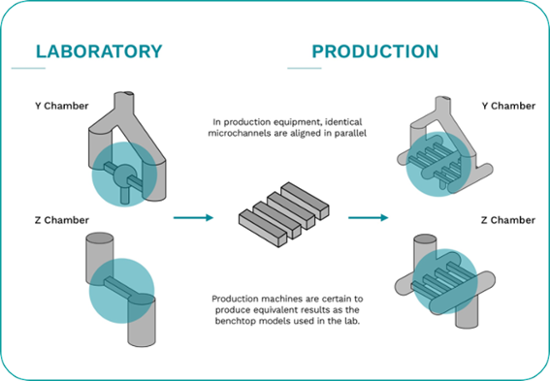
Microfluidizer® technology is easily scalable from lab to pilot scale and on to full production scale manufacturing.
Scaling up from lab equipment to full-scale production units is guaranteed, bringing cost benefits to production volumes.
This is achieved by the fact that the same Interaction ChamberTM design is used on all units - resulting in consistent quality and scalability.
The microchannels are placed in parallel on the production equipment - ensuring the same processing methods on both lab and production machines.
Recommended downloads for manufacturers looking to achieve stable nanoemulsions.